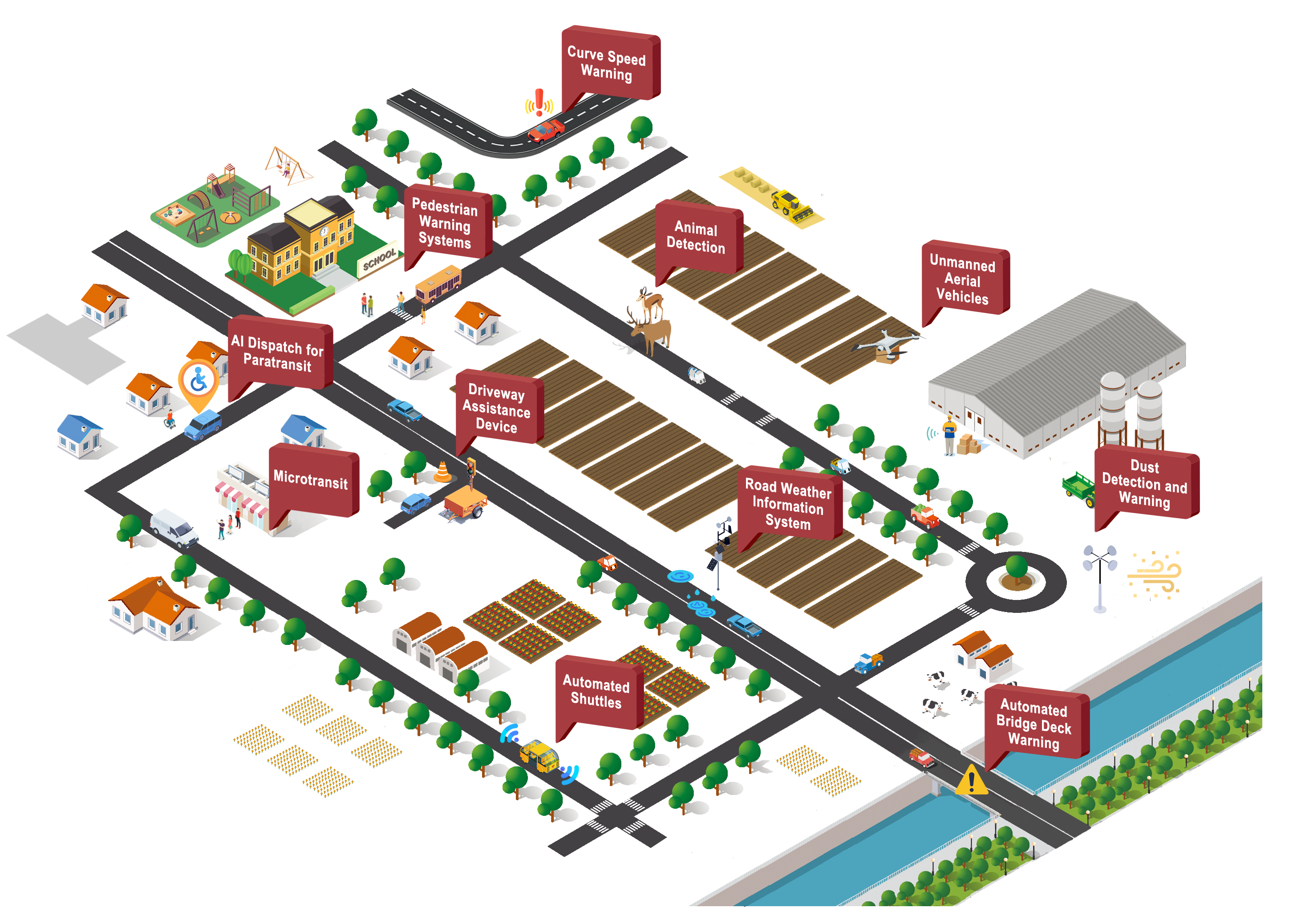
Rural areas are generally characterized by longer travel distances, lower traffic volumes, less traffic congestion, unfamiliar routes for many drivers, and more challenging terrain compared to urban areas [1]. These areas have an opportunity to use intelligent transportation systems (ITS) technologies to meet the unique needs of rural travelers. ITS is deployed in rural areas to support travelers and transportation operators in small towns, rural counties, and across interstate and regional corridors to improve mobility, safety, and quality of life for rural residents and visitors. This visualization was developed using publicly available evaluation and research studies from the Benefits, Costs, and Lessons Learned Database and shows selected technologies that help facilitate rural transportation.

| Technology or Operational Strategy | Overview | Benefit Example | Location | Year | Taxonomy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dust Detection and Warning | Dust detection and warning system, which includes overhead message boards, variable speed limit signs, closed-circuit cameras, and short-range detectors, is used to monitor dust levels and visibility on roadways and to adjust speed limits to help drivers slow down safely during dust events. | A dust detection and warning system deployed in Arizona automatically changed speed limits from 75 mph to 35 mph during dust storms, resulting in reduced average vehicle speeds of 45 mph. (2024-B01904) | Arizona, US | 2020 | Weather » Spot Weather Impact Warning (WX03) |
| Animal Detection | Animal detection systems are designed to detect large animals (e.g., deer, moose, elk) as they approach the road and warn oncoming drivers with flashing lights or messages, helping to prevent animal-vehicle collisions. | Idaho DOT used a radar and thermal camera system to detect animals on a rural road, reducing vehicle speeds up to 4.4 mph when active. (2021-B01581) | Idaho, US | 2017 | Traveler Information » In-Vehicle Signage (TI07) Traffic Management » Dynamic Roadway Warning (TM12) Vehicle Safety » Situational Awareness (VS03) |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) Dispatch for Paratransit | Paratransit provides flexible transportation options for individuals with mobility challenges who may have difficulty using fixed-route transit. AI can be applied to paratransit for dynamic, automated, and data-driven dispatching. | Prairie Hills Transit piloted AI technologies in its paratransit dispatch system in rural South Dakota. The AI-enhanced system reduced the time it takes to send trip details to the driver by over 78 percent. (2025-B01922) | Spearfish, South Dakota, US | 2024 | Traveler Information » Shared Use Mobility and Dynamic Ridesharing (TI06) |
| Microtransit | Microtransit is a flexible, on-demand transit service that uses smaller vehicles (e.g., vans) to provide shared rides. In rural areas, it may be advantageous by offering better coverage and shorter wait times than fixed-route services. | During a year-long demonstration of microtransit in Wilson, NC, ridership increased by 58 percent, from 9,000 rides in March 2021 when the service was initiated to 14,200 rides in February 2022. (2025-B01910) | Wilson, North Carolina, US | 2023 | Traveler Information » Shared Use Mobility and Dynamic Ridesharing (TI06) |
| Road Weather Information System (RWIS) | RWIS sensors provide data on road surface and local weather conditions that support safer and more efficient winter maintenance operations. This information can facilitate early hazard detection, optimize treatment actions and timing, enhance traveler information, and reduce costs. For example, RWIS are used to guide effective material spreading to ensure efficient use of salt, sand, and de-icers. | A pilot test of an intelligent salt application in Massachusetts using RWIS data reduced salt usage by 34 percent over conventional methods. (2025-B01934) | Amherst and Auburn, Massachusetts, US | 2024 | Maintenance and Construction » Winter Maintenance (MC04) Weather » Weather Data Collection (WX01) Weather » Roadway Micro-Prediction (WX04) |
| Driveway Assistance Device (DAD) | A DAD uses sensors, signals, or communication systems to control traffic coming from driveways or minor roads attempting to join an existing queue of vehicles in work zones by indicating when it's safe to merge into the main traffic stream. | A study evaluating driveways in four work zones along State Route 60, a two-lane two-way rural minor arterial, found that DADs reduced driveway waiting time by 46 percent and reduced vehicle speeds by 28 percent compared to temporary traffic signals. (2023-B01781) | Muskingum, Ohio, US | 2023 | Maintenance and Construction » Work Zone Management (MC06) Traffic Management » Traffic Signal Control (TM03) |
| Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) | UAVs, commonly known as drones, are potential alternatives to freight deliveries for meeting short-range mobility needs. | A study modeling drone deliveries showed that depot-based drone delivery led to up to 60 percent cost savings compared to truck-only delivery when servicing low demand in small areas. (2024-B01845) | Rantoul, Illinois, US | 2023 | Commercial Vehicle Operations » Freight Administration (CVO02) |
| Automated Shuttles | Automated shuttles can help people access transportation options for grocery trips, medical appointments, jobs, and social services, especially in smaller, less dense communities. | Automated shuttle pilots at Yellowstone National Park and Wright Brothers National Memorial achieved high visitor satisfaction rates of 95.4 percent and 91.9 percent, respectively. (2025-B02006) | Yellowstone National Park: Wyoming, US; Kill Devil Hills, North Carolina, US | 2022 | Vehicle Safety » Automated Vehicle Operations (VS16) |
| Pedestrian Warning Systems | A variety of ITS can be implemented to improve rural pedestrian crossings. One example is Rectangular Rapid Flashing Beacons (RRFBs), which are pedestrian-activated lights that boost visibility and driver awareness at marked, uncontrolled crosswalks. | RRFBs installed at rural crosswalks across six sites led to an increase in driver yield rates of up to 43 percent. When RRFBs were active, drivers were 2.59 times more likely to yield to pedestrians. (2023-B01776) | Vermont, US | 2023 | Vehicle Safety » Vulnerable Road User Safety (VS12) |
| Automated Bridge Deck Warning | An automated bridge deck warning system (ABDWS) uses sensors to detect moisture and temperature settings, triggering alerts to drivers (e.g. "BRIDGE ICES BEFORE ROAD") and/or automated messages to agency staff when conditions exceed system thresholds. | A deployment of ABDWS using non-invasive sensors on I-75 in Michigan observed a 35 percent reduction in the total number of crashes in icy, snowy, and slushy conditions and a reduction in crash severity. (2024-B01854) | Otsego and Cheboygan County, Michigan, US | 2020 | Weather » Spot Weather Impact Warning (WX03) |
| Curve Speed Warning | Curve Speed Warnings help prevent crashes on curves by alerting drivers who are approaching the curve at an unsafe speed based on the conditions within the curve. | Drivers using an in-vehicle curve-speed warning system with audio and visual alerts approached horizontal curves 8 percent to 10 percent more slowly than without the system at a test site in Minnesota. (2021-B01604) | St. Cloud, Minnesota, US | 2018 | Traveler Information » In-Vehicle Signage (TI07) Vehicle Safety » Curve Speed Warning (VS05) |